|
|
| RESEARCH ACTIVITIES |
 |
| Surface Plasmon Enhanced Luminescence from Silicon Nanocrystals |
 |
123. Yugo Mochizuki, Minoru Fujii, Shinji Hayashi, Takaaki Tsuruoka, and Kensuke Akamatsu
“Enhancement of Photoluminescence from Silicon Nanocrystals by Metal Nanostructures made by Nanosphere Lithography,”
Journal of Applied Physics, Vol. 106, 013517, pp. 1-5 (2009). |
| The effect of metal nanostructures prepared by nanosphere lithography
on photoluminescence (PL) properties of silicon nanocrystals (Si-ncs) is
studied. By placing Ag nanotriangles or Au nanovoids on SiO2 films containing
Si-ncs, the PL intensity is enhanced. For the sample having Ag nanotriangles,
the largest PL enhancement is obtained when the excitation wavelength coincides
with the absorption band of Ag nanotriangles. This suggests that the enhancement
of the incident field by surface plasmon polariton (SPP) excitation is
responsible for the PL enhancement. On the other hand, for the sample having
Au nanovoids, the PL enhancement is mainly made by the enhancement of effective
radiative decay rate of Si-ncs by efficient excitation and scattering of
SPPs. |
|
 |
95. Toshihiro Nakamura, Minoru Fujii, Satoru Miura, Masaki Inui, and Shinji Hayashi,
"Spontaneous Emission Rate of Si Nanocrystals on Thin Au Film,”
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, Vol. 46, No. 10A, pp. 6498-6502, October (2007). |
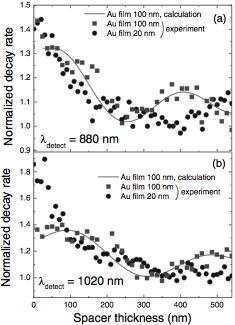
| The effect of Au films with different thicknesses (20 and 100 nm) on the
luminescence decay rate of Si nanocrystals was studied in a wide wavelength
range. For the sample with the Au thickness of 100 nm, the luminescence
decay rate oscillated depending on the distance between the Si nanocrystals
and the Au film owing to the modification of the photonic mode density
at the position of the Si nanocrystals. On the other hand, when the thickness
of the Au film was 20 nm, the oscillation was not observed and a strong
enhancement of the decay rate appeared in a small distance range. The degree
of enhancement depended on the emission wavelength. These effects are considered
to arise from a strong coupling between the electronic excitation of Si
nanocrystals and the surface plasmon polariton modes supported by the rough
Au surface. |
|
 |
P57. Nobuyuki Ishikura, Minoru Fujii, Masaki Inui, and Shinji Hayashi
"Photoluminescence Properties of Si Nanocrystals near Rough Au Films,”
Transactions of the Materials Research Society of Japan, Vol. 33, No. 1, pp. 141-144 (2008).
(Proceedings of 18th Materials Research Society of Japan Academic Symposium, Nihon University, Tokyo, December 9 (2007))
|
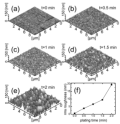
| We studied metal-enhanced photoluminescence (PL) from Si nanocrystals
(Si-ncs) placed near rough Au films. Au films with different degree of
roughness were prepared by electroless Au plating. We found that the PL
intensity and the decay rate increase as the roughness becomes large. The
PL excitation spectra revealed that the PL enhancement is the largest when
the excitation wavelength corresponds to that of the surface plasmon resonance
of rough Au films. The result combined with the emission wavelength dependence
of PL enhancement factors suggest that the PL enhancement is caused by
the enhancement of an electric field of incident light due to the excitation
of surface plasmons supported by the rough Au films and also the increase
of radiative decay rate of Si-ncs. |
|
 |
93. Eiji Takeda, Minoru Fujii, Toshihiro Nakamura, Yugo Mochizuki, and Shinji Hayashi,
"Enhancement of Photoluminescence from Excitons in Silicon Nanocrystals via Coupling to Surface Plasmon Polaritons,”
Journal of Applied Physics, Vol. 102, pp. 023506-1-6, July (2007). |
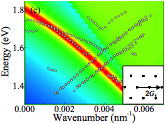
| The enhancement of photoluminescence (PL) is demonstrated from silicon
nanocrystals (Si-ncs) by strong coupling of excitons to surface plasmon
polaritons (SPPs) supported by a Au thin film. SPPs excited via excitons
in Si-ncs were Bragg scattered to photons by one- or two-dimensional gratings,
and strong and directional PL was obtained. From the angular dependence
of PL spectra, dispersion relations of electromagnetic modes involved in
the light emission process were obtained. The overall agreement between
experimentally obtained and theoretically calculated dispersion relations
confirmed that the strong and directional PL is mediated by SPPs. The PL
decay rate of Si-ncs increased by placing a Au thin film on top and the
wavelength dependence of the rate enhancement agreed well with that of
the calculated SPP excitation rate. This suggests that the observed PL
enhancement is due to efficient energy transfer from excitons to SPPs followed
by efficient scattering of SPPs to photons, resulting in the enhancement
of luminescence quantum efficiency. |
|
 |
86. Eiji Takeda, Toshihiro Nakamura, Minoru Fujii, Satoru Miura, and Shinji Hayashi,
"Surface Plasmon Polariton Mediated Photoluminescence from Excitons
in Silicon Nanocrystals,”
Applied Physics Letters, Vol. 89, 101907, pp. 1-3, September (2006). |
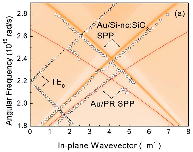
| Surface plasmon polaritons (SPPs) of a metal film can efficiently be excited
when a light emitter is placed nearby. The excited SPPs are converted to
photons by compensating for the momentum mismatch. The authors study SPP-mediated
emission from excitons in Si nanocrystals (Si-nc’s) by placing an organic
grating on a thin Au film placed near Si-nc’s. The dispersion relation
is obtained from angle-resolved photoluminescence measurements, and all
the observed modes are well explained by model calculation. The results
indicate that excitons in Si-nc’s can efficiently excite SPPs in thin metal
films and directed photoluminescence can be realized. |
|
| |
85. Kenji Imakita, Minoru Fujii, Toshihiro Nakamura, Satoru Miura, Eiji Takeda and Shinji Hayashi,
"Enhancement of Radiative Recombination Rate of Excitons in Si Nanocrystals on Au Film,”
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, Vol. 45, No. 8A, pp. 6132-6136, August (2006). |
| We investigate the time-resolved photoluminescence (PL) spectra of Si-nanocrystal
(Si-nc)-doped SiO2 on Au thin films. It is shown that PL intensity within
several tenth of µs after excitation is increased in the presence of Au
films. The data suggest that the radiative recombination rate of excitons
in Si-nc's is increased, and the degree of increase depends strongly on
the emission photon energy. We show that the enhancement is caused by the
modification of the local photonic mode density in the presence of Au thin
films. |
|
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |

|
|
|

