|
|
| RESEARCH ACTIVITIES |
 |
| Colloidal Group IV (Si, Ge) Semiconductor Nanocrystals |
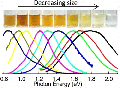 |
178. Hiroshi Sugimoto, Minoru Fujii, Kenji Imakita, Shinji Hayashi, and Kensuke Akamatsu,
"Codoping n- and p-Type Impurities in Colloidal Silicon Nanocrystals -Controlling Luminescence Energy from below Bulk Band Gap to Visible Range",
The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, Vol. 117, No. 22, pp. 11850–11857
(2013).
|
| We present a novel synthesis of ligand-free colloidal silicon nanocrystals (Si-NCs) that exhibits efficient photoluminescence (PL) in a wide energy range (0.85− 1.8 eV) overcoming the bulk Si band gap limitation (1.12 eV). The key technology to achieve the wide-range controllable PL is the formation of donor and acceptor states in the band gap of Si-NCs by simultaneous doping of n- and p-type impurities. The colloidal Si-NCs are very stable in an ordinary laboratory atmosphere for more than a year. Furthermore, the PL spectra are very stable and are not at all affected even when the colloids are drop-cast on a substrate and dried in air. The engineering of the all- inorganic colloidal Si-NC and its optical data reported here are important steps for Si- based optoelectronic and biological applications. |
|
 |
175. Hiroshi Sugimoto, Minoru Fujii, Kenji Imakita, Shinji Hayashi, and Kensuke Akamatsu,
"Phosphorus and Boron Co-doped Colloidal Silicon Nanocrystals with Inorganic Atomic Ligands",
The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, Vol. 117, No. 13, pp. 6807−6813 (2013).
|
| The surface structure of P and B codoped colloidal Si- NCs are studied
by photoluminescence (PL) in hydrofluoric acid (HF) solution and X-ray
photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). We find that codoped Si-NCs are much
more stable in HF solution than undoped, P- doped, and B-doped Si-NCs.
The PL study combined with XPS results reveal that a high B concentration
layer is formed on the surface of codoped Si-NCs and the layer acts as
a kind of inorganic atomic ligands for Si-NCs. The high B concentration
layer makes Si-NCs hydrophilic and dispersible in polar liquids. Furthermore,
the layer effectively protects Si-NCs from oxidation in solution and in
air. |
|
|
|
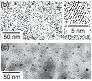 |
152. Masatoshi Fukuda, Hiroshi Sugimoto, Minoru Fujii, Kenji Imakita, and Shinji Hayashi,
Surfactant-free solution-dispersible Si nanocrystals -surface modification by impurity control
Optics Letters, Vol. 36, No. 20, pp. 4014-4016 (2011).
|
| Si nanocrystals (Si-NCs) dispersible in polar liquid without surface
functionalization by organic molecules have been realized by simultaneously
doping n and p type impurities. We show that the codoped Si-NCs are stable
in methanol for more than five months, while intrinsic Si-NCs prepared
by the same procedure form large agglom- erates. The different behavior
of the intrinsic and codoped Si-NCs in solutions suggests that doped impurities
exist on the surface of Si-NCs and the surface potential is large enough
to prevent the agglomeration. The colloidal solution of codoped Si-NCs
exhibits broad photoluminescence with the maximum in the near infrared
range (1:1–1:3 eV). |
|
|
|
|
|
| |

|
|
|

