Research Fields
- Polymer Electrolyte Fuel Cell
- Study on Performance Improvement of Evaporator used in Binary Cycle for Geothermal Sources
- Two-phase Flow Dynamics
- Heat Flow Characteristics in Heat Exchanger
- Boiling Heat Transfer Enhancement
- Condensation Heat Transfer
- Non-Newtonian Slurry Flow
- Ultrasonic Flow Measurement Technique
Laboratory introduction movie (in Japanese)
Research Topics
Polymer Electrolyte Fuel Cell
@@@@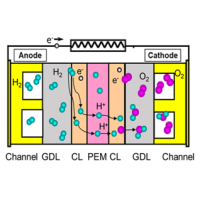
Clarification of Water Transport and the Electrochemical Characteristics in Polymer Electrolyte Fuel Cell
Water management is significantly important for PEFC performance, and clarification of the water-transport mechanisms between the PEM, GDL, and gas channels are of great concern. Furthermore, understanding the relation between the water distribution and the electrochemical characteristics are important.
In this study, neutron radiography has been employed for measuring water distribution under the PEFC operation. The water distribution are compared with the fuel cell performances and the model has been developed.
[Click here for details]
Study on Performance Improvement of Evaporator used in Binary Cycle for Geothermal Sources

Boiling Heat Transfer in Horizontal Tube Bundle
The boiling heat transfer in horizontal tube bundle will be enhanced by vapor bubbles due to bubble agitation effect.
When boiling heat transfer enhancement tubes are partially inserted at the upstream of the tube bundle, it is expected to enhance the bubble agitation effect by homogeneous small bubble flows.
In this study, tube bundle boiling experiments with boiling heat transfer enhanced tubes are conducted using HFC-245fa as the working fluid.
Thermal spray coating was applied for boiling heat transfer enhancement. The relationship between bubble flow behaviors and heat transfer characteristics is considered.
[Click here for details]
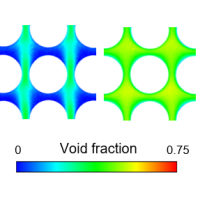
Void Fraction and Heat Transfer Characteristics around Tubes in Two-phase Flows across Horizontal Tube Bundles
It is known that bubbles motion agitates the liquid phase, resulting in increased heat transfer in the nucleate boiling region of two-phase flows.
Hence, clarification of the relation between bubbles motion and heat transfer is important for optimizing the heat exchanger.
However, the two-phase flow characteristics are affected by the geometries such as the tube alignment and the pitch-to-diameter ratio in the horizontal tube bundles.
This study has been conducted with the objective of clarifying the local characteristics of void-fraction distribution and heat transfer around tubes in two-phase flows under adiabatic conditions with different geometries of the tube bundles.
[Click here for details]

Pool Boiling Heat Transfer Enhancement by Thermal Spray Coating
Kettle-type reboilers used in geothermal binary power generation systems require boiling heat transfer enhancement and homogeneous bubble formation from the heat transfer surface.
In addition, from the viewpoint of environmental protection, the refrigerant will be replaced from HFC refrigerants such as R245fa with high GWP to HFO refrigerants such as R1233zd(E) with low GWP.
In this study, thermal spray coatings are applied to the superhard stainless steel tube used in a real binary cycle. Pool boiling experiments are conducted with hot water heating using HFC and HFO refrigerants as the working fluid.
The effect of physical properties of the working fluid on the boiling heat transfer enhancement factor to the smooth tube was evaluated.
[Click here for details]
Two-phase Flow Dynamics

Development of Two-Phase Flow Loop Thermal Control System for Space Structure
-Boiling Two-phase Flow Experiments in International Space Station-
Two-phase flow loop thermal control system for space structures is expected to be alternate system of liquid single-phase flow system for larger amount and higher heat flux of heat removal.
Although the system has some advantages such as higher heat transfer coefficient with boiling, easy temperature control by pressure control under saturation condition, the clarification of thermo-fluid dynamics of gas-liquid two-phase flows with boiling or condensation under microgravity is required to design the system.
In this study, boiling two-phase flow experiments have been successfully carried out as a JAXA project named TPF experiment under the stable microgravity condition in Japanese Experimental Module gKIBOh of International Space Station (ISS).
Gas-liquid two-phase flow behaviors were observed in the adiabatic observation section with the channel diameter of 4 mm directly connected to a heating tube. An unique flow pattern that have never been seen under normal gravity was observed.
Densely packed relatively small bubbles were flowing continuously without coalescence. Now, the two-phase flow structures are analyzed in detail to clarify the difference from those under normal gravity.
[Click here for details]

Flow Dynamics in Liquid-metal Two-phase Flow
Liquid-metal two-phase flow has larger liquid-to-gas density ration and higher surface tension than air-water two-phase flow. Hence, it is required to evaluate an applicability of existing models on liquid-metal through the experimental researches. However, the experimental data is so limited because of the difficulty of the flow measurements.
Aim of this study is clarification of flow dynamics in liquid-metal two-phase flow. Ultrasonic tomography developed in this laboratory and radiography were applied for measuring void distribution in liquid-metal two-phase flow.
[Click here for details]
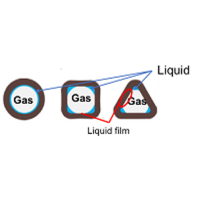
Study on Void Fraction Characteristics of Gas-Liquid Two-Phase Flows in Non-circular Mini-channels
(Square and triangular channels)
Reduction in channel diameter for increasing the heat transfer area density is required for the improvement in performance of heat exchanger used in refrigeration and air-conditioning systems.
For smaller diameter tube, the effect of surface tension on the interface structure of gas-liquid two-phases flows becomes relatively larger.
Especially, for non-circular channels, the flow characteristics will be much different from those in normal diameter tube due to liquid stagnation in the corner as shown in the left figure.
It is reported for condensing flows that the heat transfer coefficient could be improved in non-circular mini-channels due to the existence of thinner liquid film.
However, there are few report on void fraction defined as the area fraction in the cross-section.
In this study, one-component gas-liquid two-phase flow experiments in square and triangular mini-channels with the hydraulic equivalent diameter of 1 and 2 mm are conducted using FC-72 as the working fluid.
The effect of the tube diameter, cross-sectional shape, and flow direction on gas-liquid interface structure and void fraction characteristics were investigated.
[Click here for details]
Heat Flow Characteristics in Heat Exchanger
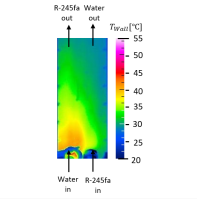
Study on Heat Flow Characteristics of Refrigerant Flow in Plate Fin Heat Exchanger
This study is deals with heat transfer and flow characteristics of refrigerant boiling flow in a plate fin heat exchanger used for heat recovery.
Since the plate fin exchanger is composed of a stack of wide flat flow channels, the heat transfer performance would depend on the phase distribution of boiling flow.
The local heat flux is also depend on the temperature difference between the refrigerant and heating medium.
Therefore, it is also important to charity the effect of the flow direction of the heat medium, i.e., the counter and parallel flow.
In this study, vertically upward boiling flows in a single-layer plate fin heat exchanger are experimentally investigated, and the effects of the flow direction of hot water and thermophysical properties of the refrigerant on the heat transfer and flow characteristics are considered.
In the experiments, the temperature distributions of the outer wall of the hot water flow channel is measured with an IR camera, and the refrigerant flow behaviors are observed by a high frame rate camera through a transparent resign wall. The right figure shows the wall temperature distribution of the hot water.
You can see the large temperature distribution that causes non-uniform heat flux distribution.
[Click here for details]
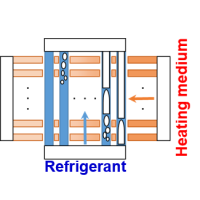
Visualization and Void Fraction Measurement of Refrigerant Flow in Cross-Flow Type Mini-Channel Evaporator
Toward the realization of a low-carbon society, high performance heat exchanger to decrease the temperature difference between fluids is required.
The increase in heat transfer area density is effective for the requirement, and is also effective for the compactness. A microchannel heat exchanger manufactured by diffusion bonding is expected as an evaporator.
Since the parallel channels of refrigerant and heating medium are in orthogonal arrangement, heat flux distribution might be not uniform due to the change of the heating medium temperature.
The non-uniform heat flux might cause a maldistribution of refrigerant flows.
In this study, boiling heat transfer experiments of HFC-134a are conducted on single layered mini-channel evaporators.
The internal boiling flows are observed by neutron radiography for stainless steel heat exchanger and high frame rate camera through a transparent window.
The time average void fraction distributions are measured from the neutron radiographs. Moreover, some rib patterns of the refrigerant channel are designed to obtain the homogenous phase distribution.
[Click here for details]
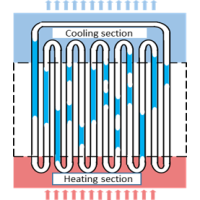
Study on Heat Transfer Characteristics on Pulsating Heat Pipe
Pulsating heat pipes has narrow channels fold the heating and cooling sections many times in a flat plate.
Conventional heat pipes use the capillary force to drive the working fluid, but the pulsating heat pipe transfers the heat by pulsating the working fluid due to the pressure difference between the heating and the cooling section.
In addition, pulsating heat pipes are considered to have higher heat transfer performance than conventional heat pipes by simultaneously transferring sensible heat and latent heat.
In this study, focuses on the heat transfer characteristics of the pulsating heat pipe and investigates the effect of the working fluid behavior on the heat transfer.
[Click here for details]
Boiling Heat Transfer Enhancement
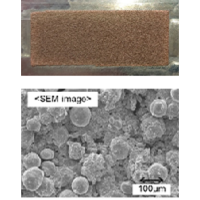
Study on the Effect of Heating Surface Structure on Subcooled Flow Boiling Heat Transfer in Horizontal Narrow Channel
Generation, detachment and flow behaviors of vapor bubbles in subcooled boiling two-phase flows are complex phenomena with boiling and condensation.
Therefore, it is required to clarify the heat transfer characteristics through experimental researches.
Although an increase in nucleation site density is efficient for nucleate boiling heat transfer enhancement, the heat transfer enhancement might decrease critical heat flux(CHF), because higher boiling heat transfer coefficient can be obtained by larger vaporization rate near the surface, and the larger vaporization rate might lead to the departure from nucleate boiling (DNB) due to bubble coalescences.
In this study, smooth surface and thermal spray coated surface were used as the heating surface.
The purpose of this study is to clarify the effect of the heat transfer surface structure and physical properties of the working fluid on boiling heat transfer characteristics and gas-liquid interface structure during subcooled flow boiling.
[Click here for details]
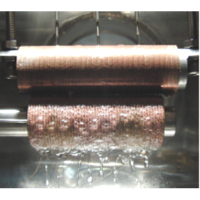
Heat Transfer Enhancement of Falling Film Evaporation
Since most of refrigerant used in refrigeration and air conditioning systems has high global warming potential (GWP), the charging amount of refrigerant is required to be reduced.
Falling film evaporator is expected as a substitute of typical flooded evaporator because it can operate with less refrigerant.
The important issues to improve the heat transfer performance are to avoid dryout for thin liquid film thickness under high heat flux or low mass flow rate conditions, and to reduce the wall superheat for the onset of nucleate boiling for thick liquid film thickness under high mass flow rate condition.
To suppress the liquid entrainment in nucleate boiling is also important issue. Therefore, heat transfer tubes need to have a functional surface.
In this study, a porous structure processed by thermal spraying is applied to the heat transfer surface. The heat transfer performance of falling film evaporation is experimentally evaluated for various refrigerants.
[Click here for details]
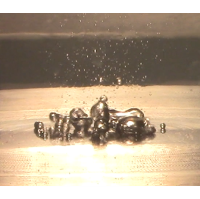
Boiling Heat Transfer Enhancement in Nanofluid
Nanofluid is a fluid suspended with nano-order particles. It is known that boiling heat transfer increases using nanofluid in comparison to that in the pure fluid.
This may be occurred because of the change of the fluid properties, and/or the particle depositions. However, the mechanisms and the optimizations of the nanoparticle condition have not been fully understood.
Aim of this study is clarification of mechanism of the boiling heat transfer enhancement using nanofluid and development of passively controlling the heat transfer enhancement using a magnetic field.
[Click here for details]
Condensation Heat Transfer

Heat transfer characteristics in a Quadrilobed tube
When high boiling point refrigerants are used for heat pump hot water supply system, the water heater operates as a condenser, and deformed tubes are often used to improve the heat transfer performance.
Quadrilobed tube with a 5 parallel paths consisting of four leaves and one core is used.
Flows in the leaf-like channels are expected to cause condensing heat transfer enhancement, because liquid film on the channel side becomes thin due to liquid accumulation in the corner. In this study, condensation heat transfer characteristics in a quadrilobed tube are investigated.
Moreover, to clarify the effect of the channel shape on condensing heat transfer, experiments for a triangular channel simulating the leaf-like channel are conducted, and heat transfer coefficients and void fraction at an adiabatic section are measured.
[Click here for details]
Non-Newtonian Slurry Flow
Study on Thermal Flow Characteristics of Non-Newtonian Slurry Flow
Sharing the waste heat from factories in the area is effective in reducing primary energy consumption, but heat transport at high energy density without temperature drop is necessary.
The PCM slurry in which phase change materials (PCM) are enclosed in hard shell capsules and dispersed in fluid is proposed. Realization of heat transport by PCM slurry requires the elucidation of heat exchange characteristics during heating and cooling.
The purpose of this study is to elucidate the thermal flow characteristics of slurry with hard shell capsules.
Surfactant is added to disperse hard shell capsules and become non-Newtonian fluid. In the experiment, we evaluate heat transfer characteristics and pressure loss characteristics during heating for non-Newtonian slurry flow in a pipe.
[Click here for details]
Ultrasonic Flow Measurement Technique
Development of an Ultrasonic Tomography
Ultrasonic tomography is a powerful tool for measuring two-phase flow phenomena. It has been developed for measuring void distribution based on the ultrasonic reflection methods.
It is essential to improve the time resolution for evaluating the time-dependence phenomena.
In this study, we employed a wide-angle sensor for fan shaped ultrasonic beam. A tomography system based on the reflection method was developed using the 8 sensors.
The system has been tested for bubble column with inner diameter of 50 mm with time-resolution of 1 ms. Improvement of the system and the reconstruction algorithm has been carried out.
[Click here for details]
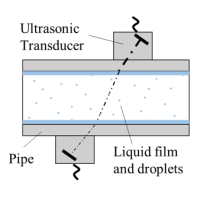
Measurement of Steam Flowrate using Clamp-on Ultrasonic Flowmeter
To achieve efficient energy management in industrial plants, it is crucial to measure the steam flow rates at the various points of consumption.
Clamp-on time-of-flight ultrasonic flowmeters are useful devices to measure the steam flow rates in existing pipes. However, it is difficult to accurately measure the steam flow rates using existing ultrasonic flowmeters.
In this study, a new signal processing method, ultrasonic transducers, and the measurement system have been developed for measuring wet steam flow rate.
[Click here for details]
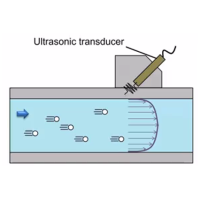
Development of Advanced Ultrasonic Flowmeters
@In transit-time ultrasonic flow meters (TOF), the flow rate is derived from the transit time of an ultrasonic pulse between two ultrasonic transducers.
To convert the transit time into flow rate, a profile factor (PF) is required. Because the PF strongly depends on the velocity profile, a precise calibration of the PF is essential to the accuracy of the TOF.
Hence, a field calibration, referred to as on-site calibration, is desirable.
In this study, a hybrid ultrasonic flow meter that helps calibrate the TOF using ultrasonic Doppler velocity profile method (UDV) has been proposed for on-site calibration by integrating the velocity profiles over the cross-sectional area of a pipe.
Furthermore, a new approach for clamp-on ultrasonic flowmeter has been developed for measuring the flow rates from outside of existing pipes.
[Click here for details]